Functions In JavaScript
What are Functions? What is their role in JavaScript?
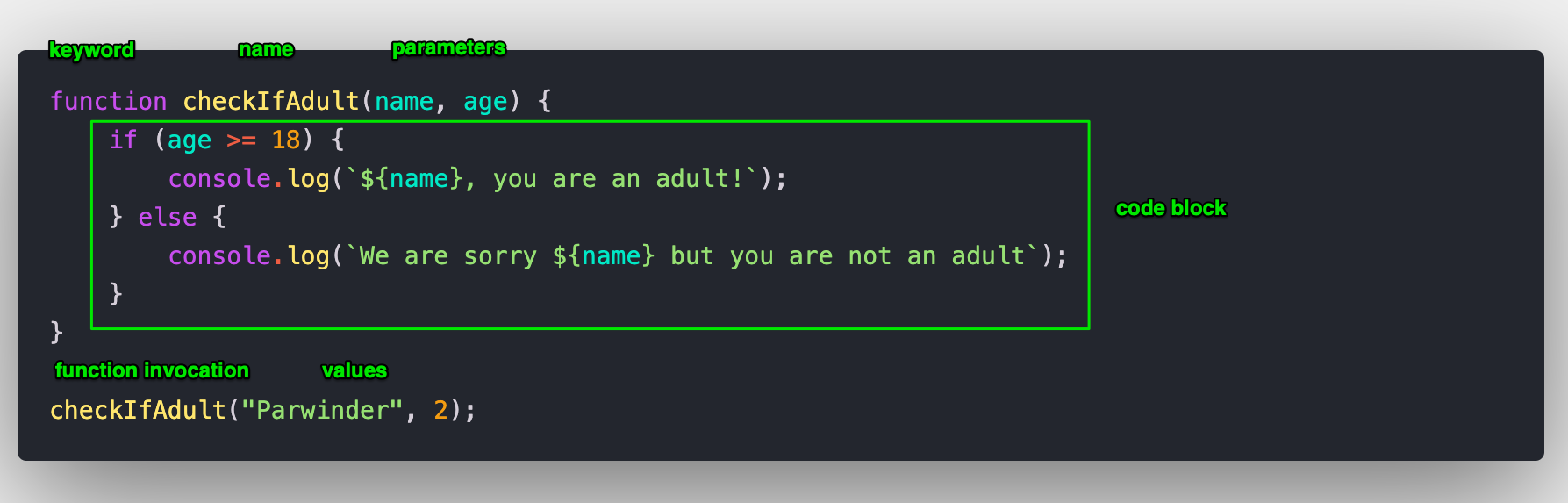
A function is a JavaScript code block that can be executed by calling/invoking it. A function has the following essential parts:
- It is declared using the
functionkeyword. - The function name then follows it. This is the name that will be used to call the function.
- You can pass arguments to a function. These are values that could be dynamic.
- The arguments are assigned to parameters of the function and are encapsulated in round brackets
() - This is followed by the code block that will be executed whenever the function is called.
- The code block is surrounded by curly braces
{}
A function is used to create reusable code blocks. If you a have piece of code that is to be executed multiple times, it is a good idea to convert it into a function.
Function Returns
A function can return you something once it has finished executing the code. This is not always the case. Sometimes functions execute the code and end.
Function with return:
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b; // You return the value using return keyword
}
const x = sum(2,5);
const y = sum(7,9);
console.log(x); // 7
console.log(y); // 16
Function without return:
console.log("Hello World!");
// Hello World
// undefined
If you run the above example in your browser console, you would see that even though the statement “Hello World” is printed in the console, the function is not returning anything. That is why you would see your browser print out undefined after the statement.
JavaScript in-built functions
You don’t always have to write your functions. JavaScript comes with a ton of functions that are ready to use.
console.log(parseInt()); // NaN (Not a number)
console.log(parseInt("234xyz")); // 234, parseInt ignore non integer
console.log(Math.random()); // 0.00746544513267
console.log(Date.now()); // 1590557812411